What is Glycemic index (GI) ?
Understanding the Glycemic Index (GI)
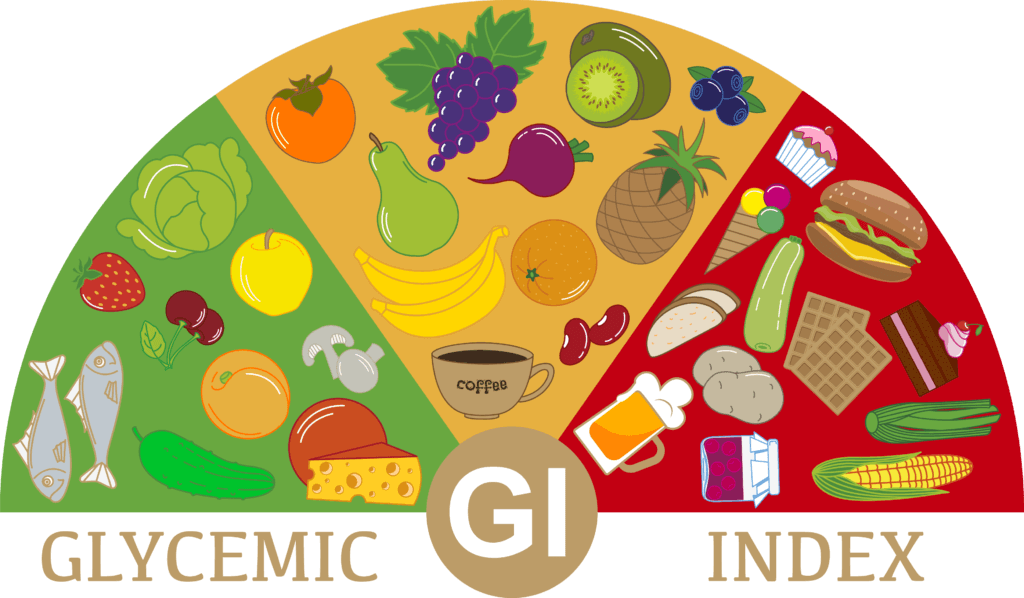
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure used to determine how much specific foods increase blood sugar levels. It is a numerical value assigned to foods on a scale of 0 to 100. The GI ranks foods based on their potential to raise blood sugar levels. Foods are classified as low, medium, or high glycemic foods based on their GI value
How the Glycemic Index Works
The GI of a food is determined by how quickly and how much it raises blood glucose levels compared to pure glucose, which is given a GI value of 100. Foods with a high GI cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels, while foods with a low GI cause a slower and more gradual rise in blood sugar levels
Factors Affecting the Glycemic Index
Several factors can influence the GI of a food, including:
- Carbohydrate Quantity and Type: The quantity and type of carbohydrates in a food primarily determine its GI. Foods with higher carbohydrate content and simple carbohydrates tend to have a higher GI
- Food Preparation and Processing: The way a food is cooked or processed can affect its GI. Generally, cooking foods for longer periods or processing them can increase their GI.
- Fat and Protein Content: The presence of fat and protein in a food can lower its GI. These macronutrients slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, resulting in a slower rise in blood sugar levels
Ripeness and Processing: The ripeness of fruits and the degree of processing of foods can impact their GI. Riper fruits and more processed foods tend to have a higher GI
Using the Glycemic Index
The GI can be a useful tool for managing blood sugar levels, particularly for individuals with conditions like diabetes. Here are some ways the GI can be used:
Food Selection: Choosing foods with a lower GI can help regulate blood sugar levels. Low GI foods include whole grains, legumes, non-starchy vegetables, and lean proteins
Meal Planning: Incorporating a variety of low to medium GI foods into meals can help create balanced and blood sugar-friendly meals
- Combining Foods: Combining high GI foods with low GI foods can help moderate the overall impact on blood sugar levels. For example, pairing a high GI food with protein or healthy fats can slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates
- Individual Considerations: It's important to note that the GI is not the only factor to consider when managing blood sugar levels. Individual responses to different foods can vary, and other factors such as portion sizes, overall diet, and medication should also be taken into account
Remember, the GI is just one tool in managing blood sugar levels, and it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice and guidance.
Releted FAQ's

5 Best Dharamshalas in Ayodhya Near Ram Mandir
01 Jan 2025

Who Are the Top 5 ENT Specialists in Kanpur?
28 Nov 2024

Invest Smart: Why Ultima 107 Is best Low-Rise Residential Project ?
16 Sep 2024
Top 5 Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad
07 Sep 2024

Who is Top 10 Immigration Consultants in Dubai ?
16 Aug 2024

What does LGBTQ mean?
13 Jul 2024
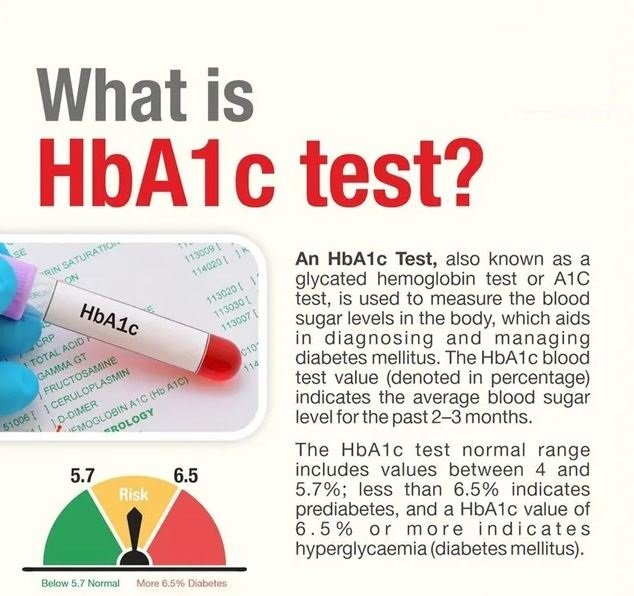
What is HbA1c test ?
03 Jul 2024

Which are the Top 10 Budget Hotel in Ayodhya near Ram Mandir ?
02 Jul 2024

Which are the top 10 travel agency in ayodhya ?
02 Jul 2024

How to control sugar?
27 Jun 2024
Our Categories
Medical: Doctors , Endocrinologist , Neurologist , Pediatrician , Dermatologist , Gastroenterologist , Orthopedic , Cardiologist , Gynecologist , Physicians , Nephrologist , Surgeon , ENT specialist , Psychiatrist , Oncologist , Radiologist , Pulmonologist , Dentist , Hematologist , Eye Specialist , Plastic Surgeon , Veterinary , Laparoscopic Surgeon , Urologist , IVF , Neonatologist , Physiotherapy , Liver Transplant , Neurosurgeon , Eye specialist , Orthopedic Surgeon Hospitals , Eye Hospital , Orthopedic , Heart , Cardiology , Clinic , Homeopathy Clinic , IVF Treatment , Brain & Spine Centre , Multispecialty Hospital , Dental Clinic , Dermatologist , Ayurvedic Hospital Pathlabs , Veterinary , Laparoscopic Surgeon , Clinic , Homeopathy Clinic , Urologist , Neurosurgeon , Dental Clinic , Dermatologist , Eye specialist , Ayurvedic Hospital , Diagnostic Center
Real Estate: Shoping Mall , Residential , Commercial , Plots , Builders and Developers , Upcoming Projects , Agents , Lawyer , Photographer , Construction Company
Education: Schools , Boarding , CBSE , ICSE , Up Board , International , Play School , Driving School Colleges , Engineering , Law , Medical Collage , DLED , B.Ed Coaching , Competitive , Classes University , Courses , Digital Marketing , English Epeaking , IT Training , English Speaking Digital Marketing , English Epeaking , IT Training
Hotels: Resort , Motel , Guest House , Paying Guest , 7 Star , 3 Star , 5 Star , Home Stay , Dharamshala , Farmhouse , 4 Star
Health And Beauty: Beauty Parlour , Gym , Spa , Hair Transplant , Weight Loss , Barber , Makeup Artist
Home and Service: Carpenter , Ro Service , Internet , Electrician , Caterers , Wedding Planner , Mineral Water Supplier , Plumbers , Other , Lawyer , Photographer Dairy Equipment , Insurance , Welding works , Ac Service
Park: Water Park , Amusement , Trampoline , Snow , Adventure